This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
Understanding P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC: Causes, Diagnosis, and Solutions GuideMechanic.Com In the world of automotive diagnostics, Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) play a vital role in identifying and resolving issues within a vehicle’s complex systems.
One such code, P3000, falls under the category of manufacturer-controlled DTCs. Unlike generic codes that are standardized across all vehicles, manufacturer-controlled DTCs can vary depending on the automaker, making them more specific and sometimes more challenging to diagnose.
In this article, we will explore the P3000 code, what it means, the common causes behind it, how to properly diagnose it, and effective repair solutions.
See Also: P3200 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
What Is DTC P3000?
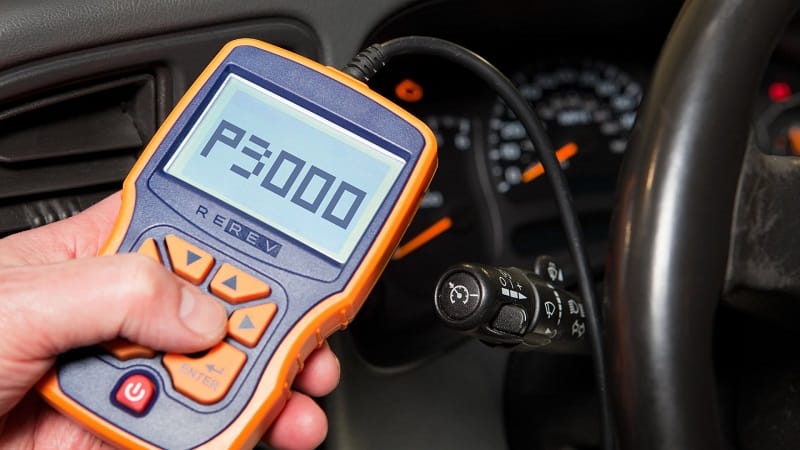

The P3000 DTC is classified as a manufacturer-specific trouble code related to the hybrid battery control system. It is most commonly found in hybrid vehicles, particularly Toyota and Lexus models.
The code indicates that the battery control system has detected an irregularity, but the nature of the irregularity can vary depending on the vehicle model and manufacturer.
In Toyota hybrid vehicles like the Prius, the P3000 code usually refers to a fault in the hybrid battery control module or an issue with the data communication between the hybrid battery and the engine control unit (ECU).
While the code alone does not pinpoint the exact problem, it signals that further investigation is required into the hybrid battery system.
Generic Definition vs Manufacturer-Specific Interpretation
A generic OBD-II scanner might define P3000 as “Battery Control System Malfunction.” However, the manufacturer-specific interpretation provides deeper insights. For instance:
- Toyota Prius (2001–2009): P3000 indicates a malfunction in the HV (High Voltage) Battery Control System. Additional subcodes (called INF codes or information codes) are usually required to pinpoint the exact fault.
- Lexus RX400h / Toyota Highlander Hybrid: The code may relate to cooling fan failure, battery overheating, or HV battery module imbalances.
This highlights the importance of using an OEM-level scan tool or software that can access manufacturer-specific data.
P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
Common Causes of P3000 Code
There are several potential causes for the P3000 code. These include:
- Faulty Hybrid Battery Pack
- Over time, hybrid battery cells degrade. A weak or imbalanced battery module can trigger the P3000 code.
- Battery Cooling System Issues
- The battery cooling fan may be obstructed, dirty, or completely failed. Poor cooling leads to overheating, which the control module detects as a fault.
- Malfunctioning Battery Control ECU
The ECU that monitors and manages the hybrid battery system may malfunction, send incorrect signals, or fail to communicate with the vehicle’s main ECU.
Wiring Problems
Corroded or damaged wires between the hybrid battery and control units may disrupt signals, leading to communication errors.
Poor Ground or Loose Connections
A loose connector or ground wire can cause intermittent failures or loss of data transmission.
Outdated Software
In some cases, outdated firmware in the hybrid control module may misinterpret normal battery fluctuations as faults.
Symptoms Associated With P3000
When the P3000 DTC is present, the following symptoms may occur:
- Illuminated Check Hybrid System / Check Engine Light
- Poor fuel economy
- Reduced acceleration or performance
- Hybrid battery warning light
- Inability to start or drive the vehicle in some severe cases
Note that these symptoms often overlap with other hybrid system DTCs, so additional codes should be checked and considered in the diagnosis.
P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
Diagnosis of P3000 Code

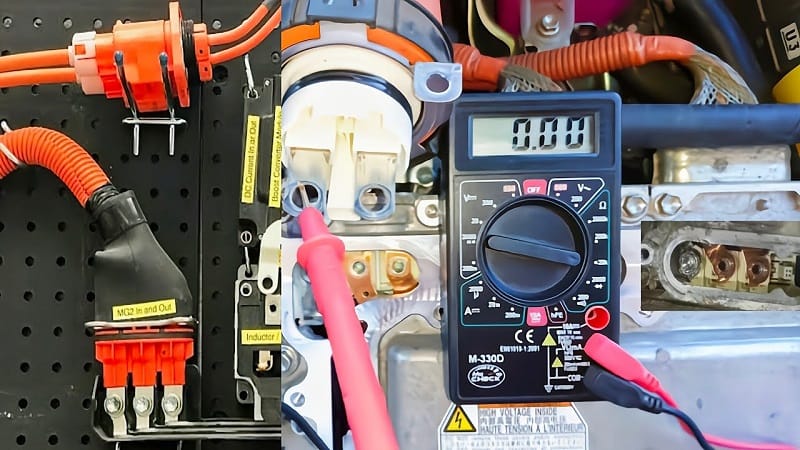
Proper diagnosis requires a methodical approach, ideally performed using a manufacturer-specific diagnostic tool (e.g., Techstream for Toyota/Lexus). Here are the general steps:
Read and Record All DTCs
Scan the entire vehicle for stored and pending DTCs. Pay special attention to any INF codes associated with P3000.
Inspect Hybrid Battery Data
Use the scan tool to view real-time data from each battery block. Look for voltage imbalances, temperature spikes, or sudden voltage drops.
Test the Battery Cooling Fan
Ensure the fan operates correctly, is free of debris, and activates under load or high-temperature conditions.
Inspect Wiring and Connectors
Check for corrosion, loose connections, or damaged wires between the hybrid battery ECU and the main ECU.
Check HV Battery Control ECU
If all else seems functional, the hybrid battery ECU itself may need to be tested or replaced.
Verify System Software
Consult TSBs (Technical Service Bulletins) or manufacturer updates to determine whether a software update is recommended.
P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
Repair and Solutions
Depending on the root cause, the following repairs may resolve the P3000 code:
Replace Hybrid Battery Modules
If testing reveals one or more failing battery blocks, replacing individual modules or the entire battery pack may be necessary.
Clean or Replace Cooling Fan
Ensure the battery cooling fan is clean, free of blockages, and functional. Replace if faulty.
Repair or Replace Wiring
Fix any damaged wires or connectors to restore proper communication between ECUs.
Replace Battery Control ECU
In cases where the ECU is faulty, replacement and reprogramming may be required.
Software Update
Perform any recommended software updates using OEM tools to prevent false detections.
Clear Codes and Test Drive
After repairs, clear all DTCs and perform a test drive under various conditions to confirm the issue is resolved.
P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC
Preventive Measures
Hybrid vehicles require regular maintenance and monitoring to prevent DTCs like P3000. Here are a few best practices:
- Monitor hybrid battery health through periodic diagnostics.
- Clean air filters and cooling vents to prevent overheating.
- Use high-quality replacement parts for battery and ECU repairs.
- Avoid prolonged high-speed driving in hot climates if the cooling system is marginal.
Conclusion
The P3000 Manufacturer Controlled DTC is a critical code in hybrid vehicles that indicates issues within the battery control system.
Although its exact meaning may vary depending on the automaker, it is commonly associated with hybrid battery malfunctions, communication errors, or control module failures.
Accurate diagnosis requires manufacturer-level tools, a good understanding of the hybrid drivetrain, and sometimes the interpretation of INF codes for deeper insight.
For technicians and hybrid vehicle owners alike, understanding the nature of this code and responding promptly can prevent further damage, reduce repair costs, and ensure the continued efficiency of the hybrid powertrain.
As hybrid technology continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive remains the key to successful vehicle maintenance and repair.
- Custom Lifted Diesel Trucks for Sale - December 20, 2025
- New Lifted Diesel Trucks for Sale - December 19, 2025
- Old Lifted Diesel Trucks for Sale - December 18, 2025
