This post contains affiliate links. This means I will make a commission at no extra cost to you should you click through and make a purchase [ “As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.” ]. Read the full disclosure here.
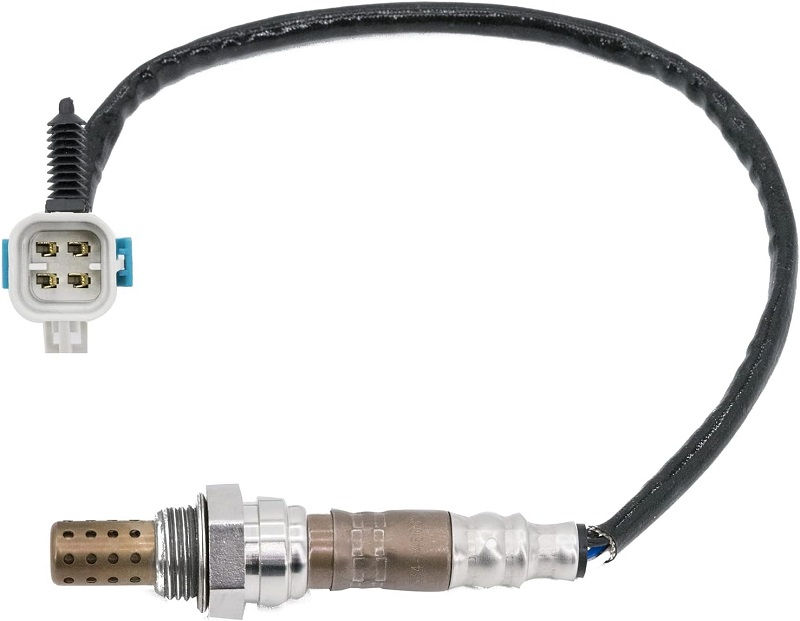
Understanding P0043 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 3) GuideMechanic.Com In the realm of automotive diagnostics, the emergence of trouble codes serves as a roadmap for identifying and rectifying issues within a vehicle’s complex systems.
One such code, P0043, pertains to the HO2S (Heated Oxygen Sensor) Heater Control Circuit Low for Bank 1 Sensor 3. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of P0043, shedding light on its significance, underlying causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and potential solutions.
See Also: P0041 Downstream Oxygen Sensors Swapped From Bank To Bank
P0043 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
Decoding P0043:

P0043 is categorized as a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), indicating a detected low voltage condition in the HO2S Heater Control Circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 3.
In simpler terms, it signifies an anomaly in the heating element of the oxygen sensor situated within the exhaust system of the vehicle.
Understanding the Oxygen Sensor:
Before delving into the specifics of P0043, it’s crucial to grasp the pivotal role of oxygen sensors in modern vehicle engines.
Oxygen sensors, also known as O2 sensors, are tasked with monitoring the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases. This data is pivotal for the Engine Control Unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture, facilitating optimal combustion efficiency and emission reduction.
P0043 HO2S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
Importance of the Heater Circuit:
Oxygen sensors are equipped with a heating element to expedite reaching operational temperature, particularly during cold starts when exhaust temperatures are low.
The heater circuit ensures swift activation of the oxygen sensor, enabling prompt and accurate readings for effective engine operation and emission control from the moment the vehicle is started.
Bank 1 Sensor 3 Location:
In engines with multiple cylinders arranged in a V configuration (e.g., V6, V8), two banks of cylinders are typically present: Bank 1 and Bank 2.
Bank 1 denotes the side of the engine where the number one cylinder is located. Sensor 3 refers to the third oxygen sensor in the exhaust system of Bank 1, typically positioned downstream after the catalytic converter.
Common Causes of P0043:
Several factors can contribute to the occurrence of the P0043 DTC, including:
Faulty Oxygen Sensor:
A malfunctioning oxygen sensor, often due to wear and tear or internal component degradation, can lead to a low voltage condition in the heater circuit.
Heater Circuit Malfunction:
Issues such as wiring faults, damaged connectors, or a defective heater circuit can impede the proper functioning of the oxygen sensor’s heating element, resulting in a low voltage reading.
ECU or PCM Anomalies:
Rarely, glitches or malfunctions within the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) can disrupt the oxygen sensor’s heater control circuit, triggering the P0043 code.
Exhaust System Irregularities:
Any leaks or damage in the exhaust system upstream of the oxygen sensor can introduce false air, affecting sensor readings and contributing to a low voltage condition.
Symptoms of P0043:
When the P0043 DTC is detected, the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system will illuminate the Check Engine Light (CEL) on the dashboard. Additionally, the following symptoms may manifest:
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Impaired engine performance
- Rough idling or stalling
- Elevated emissions
Diagnosing and Rectifying P0043:
Addressing the root cause of the P0043 code necessitates a systematic diagnostic approach, often involving diagnostic tools like scan tools or multimeters. Here’s a generalized outline of the diagnostic and repair process:
Comprehensive Code Scan:
Begin by scanning for additional trouble codes to gain comprehensive insights into potential related issues.
Wiring and Connector Inspection:
Thoroughly examine the wiring harness and connectors associated with the oxygen sensor’s heater circuit, checking for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
Heater Circuit Resistance Testing:
Utilize a multimeter to measure the resistance of the oxygen sensor’s heater circuit, comparing the readings against manufacturer specifications to identify deviations indicating malfunction.
Oxygen Sensor Evaluation:
If the heater circuit passes inspection, assess the oxygen sensor itself, examining its output voltage or responsiveness to changes in exhaust gas composition.
Exhaust System Examination:
Inspect the exhaust system for leaks or damage that could compromise sensor readings and contribute to the low voltage condition.
Component Replacement:
Based on diagnostic findings, replace any faulty components, be it the oxygen sensor, wiring harness, connectors, or fuses.
Code Clearance and Testing:
After effecting repairs, clear the trouble codes from the vehicle’s memory using a scan tool. Subsequently, conduct a test drive to ensure the issue has been successfully addressed and the CEL remains extinguished.
Conclusion:
P0043, indicative of a low voltage condition in the HO2S Heater Control Circuit for Bank 1 Sensor 3, presents a diagnostic challenge requiring meticulous troubleshooting for resolution.
Understanding the pivotal role of oxygen sensors, heater circuits, and exhaust system components is paramount for effective diagnosis and rectification of this issue.
By adhering to a systematic diagnostic process, automotive technicians can pinpoint the underlying cause of the problem and restore the vehicle’s performance and emission control functionalities.
See Also: P0042 HO2S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
- P007F 62 Code Range Rover - June 10, 2024
- P007F Ford Focus: Causes, Diagnosis, and Solutions - June 5, 2024
- P0080 Ford: Causes, Diagnosis, and Solutions - May 31, 2024